Insect Pest Management: Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture

Insect pest management is a critical component of modern agriculture. As farms face increasing challenges from insect infestations, effective management strategies are essential to safeguard crops, enhance yield, and promote sustainable farming practices. This article delves deep into the concept of insect pest management, explores various strategies, and discusses the intersection of technology and farming equipment to combat pest challenges effectively.
Understanding Insect Pest Management
The field of insect pest management involves the use of various techniques to control pests while minimizing environmental impact. The ultimate goal is to reduce pest populations to acceptable levels without resorting to harmful chemicals that can adversely affect the ecosystem and human health.
The Importance of IPM (Integrated Pest Management)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control. It relies on a combination of biological, cultural, physical, and chemical tools to manage pests sustainably. Key principles include:
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular scouting and monitoring of pest populations help farmers make informed decisions.
- Threshold Levels: Establishing action thresholds to determine when control measures are necessary.
- Control Methods: Utilizing a combination of biological controls, cultural practices, and judicious pesticide application.
Key Strategies in Insect Pest Management
Effective insect pest management requires a diverse array of strategies to combat different types of pests. Let’s explore several advanced methods used in the field:
1. Biological Control
Biological control involves the use of natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations. This method is particularly effective for certain types of pests and is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. Examples include:
- Introducing ladybugs to control aphid populations.
- Utilizing nematodes to attack root-dwelling pests.
- Employing beneficial insects and microorganisms that suppress harmful insects.
2. Cultural Practices
Cultural practices encompass a broad range of agronomic techniques that can minimize pest establishment and survival. Key practices include:
- Crop Rotation: Helps break the life cycle of pests.
- Proper Sanitation: Keeping fields free from debris that can harbor pests.
- Choosing Resistant Varieties: Planting pest-resistant crop varieties can reduce infestation levels significantly.
3. Mechanical and Physical Controls
Mechanical and physical controls are often the first line of defense. These strategies include:
- Barriers: Such as row covers or netting to prevent pests from reaching crops.
- Handpicking: Manual removal of pests can be effective for small infestations.
- Traps: Using pheromone traps can help catch and monitor pest populations.
4. Chemical Controls
While chemical controls should not be the first choice, they are sometimes necessary. Integrated Pest Management emphasizes the careful use of pesticides. Considerations include:
- Selecting targeted pesticides with minimal environmental impact.
- Implementing proper application techniques to reduce drift and runoff.
- Following label instructions to ensure safe and effective use.
Leveraging Technology in Insect Pest Management
The integration of technology in insect pest management has revolutionized farming practices. Smart agriculture tools empower farmers with information and analytics to make informed decisions. Key technological innovations include:
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture utilizes GPS and IoT devices to monitor crop health and pest populations in real-time. This data-driven approach allows for targeted interventions, reducing chemical use and improving environmental health.
2. Remote Sensing and Drone Technology
Drones equipped with imaging technology can survey fields quickly, identifying pest hotspots and areas requiring attention. This technology plays a critical role in early detection and intervention.
3. Data Analytics
By analyzing historical data related to weather, pest populations, and crop health, farmers can predict pest outbreaks and take preventive measures. This approach minimizes losses and ensures a healthier crop yield.
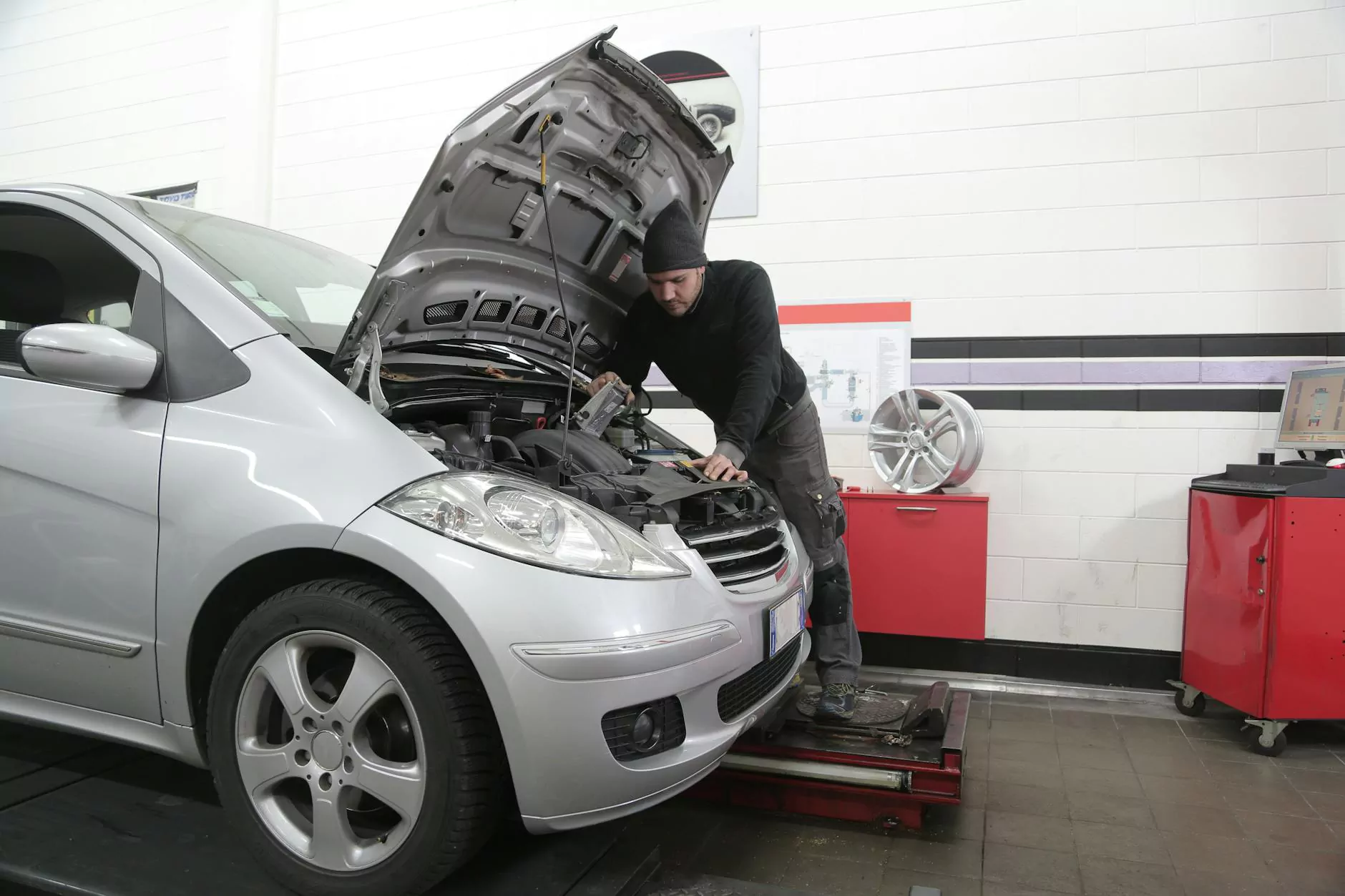
Farm Equipment and Maintenance in Pest Management
Proper farming equipment maintenance is crucial for effective insect pest management. Well-maintained equipment ensures precision in pesticide application and other pest control strategies. TSGC Inc. provides expert farm equipment repair services to ensure your machinery is always in top condition. Regular maintenance checks can prevent:
- Malfunctioning sprayers that may lead to uneven pesticide distribution.
- Leakages that can result in environmental contamination.
- Overuse of machinery that leads to soil compaction and reduced crop health.
Conclusion: The Future of Insect Pest Management
The future of insect pest management lies in the continuous adaptation of sustainable practices combined with technological advancements. Farmers are increasingly moving towards eco-friendly methods that not only control pests but also enhance the resilience of ecosystems.
Investing in proper farming equipment and maintaining it through reliable services, like those offered by TSGC Inc., is essential to achieving successful pest management outcomes. Together, we can create a sustainable future for agriculture that balances productivity with environmental stewardship.
Get Involved and Stay Informed
As we continue to learn and adapt, staying informed about the latest practices in insect pest management and advancements in farming equipment is crucial. Engage with experts, attend workshops, and utilize resources available through organizations dedicated to sustainable agriculture.
Join the movement towards sustainable farming, and let’s work together to ensure healthy crops and a vibrant ecosystem for generations to come.