Understanding the Parts of Hydraulic Excavators
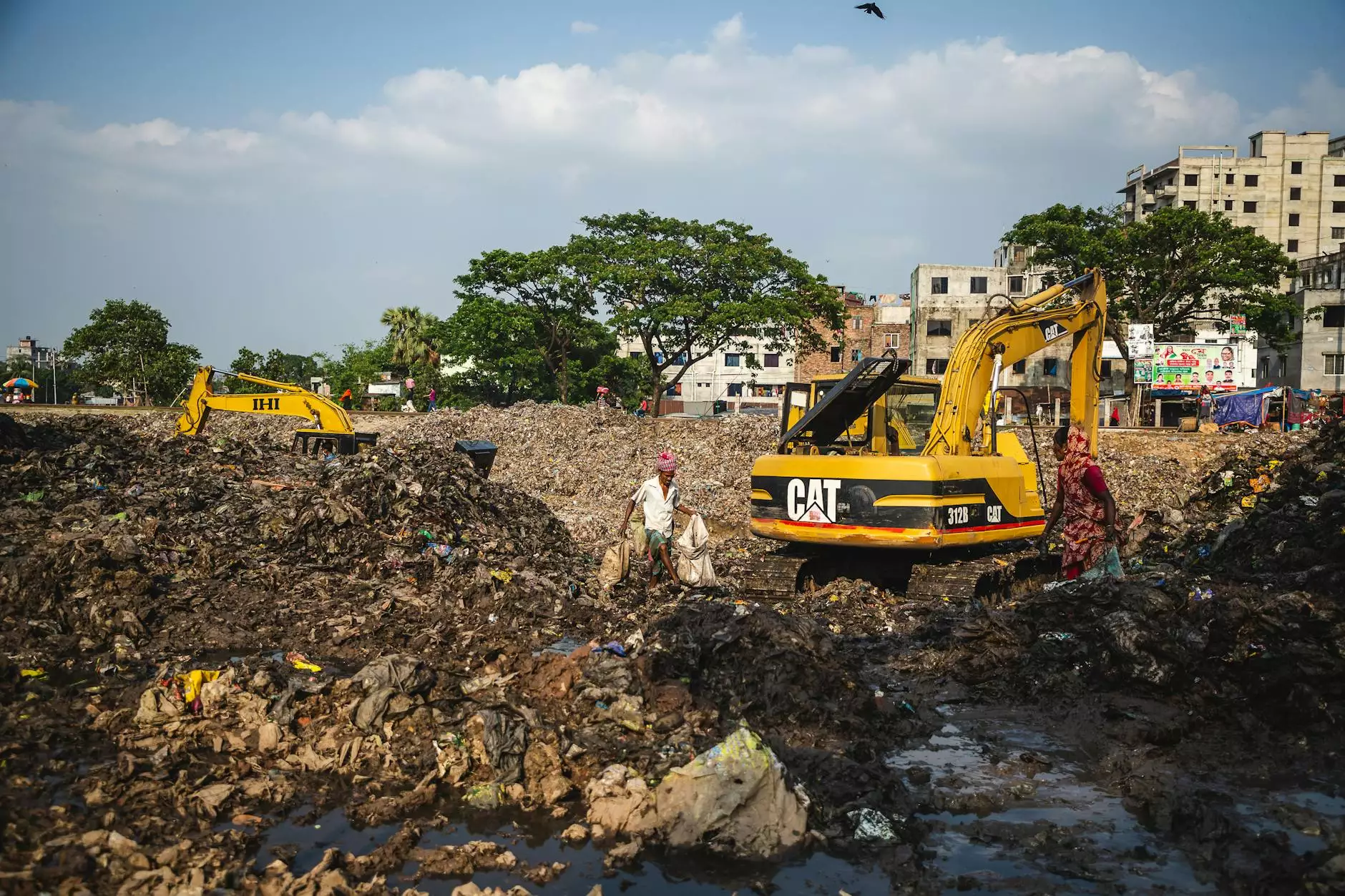

Hydraulic excavators are a marvel of engineering, designed to perform a variety of heavy-duty tasks with incredible efficiency. Whether you're involved in construction, mining, or any other industry that demands precision excavation, understanding the parts of hydraulic excavators is crucial. This comprehensive guide dives deep into these components, explaining their functions, significance, and maintenance tips.
What is a Hydraulic Excavator?
A hydraulic excavator is a heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, a dipper (or stick), a bucket, and a rotating platform known as the house. It utilizes hydraulic mechanisms to lift heavy loads and dig deep into the ground. Excavators are versatile and can be equipped with various attachments for different tasks.
The Main Components of Hydraulic Excavators
Understanding the individual parts of hydraulic excavators is vital for professionals working with these machines. Below, we've broken down the primary components into easy-to-understand sections:
1. The Boom
The boom is a long arm that extends from the house of the excavator. It provides the main lifting power necessary for excavating materials. Different types of booms, such as straight booms and curved booms, are available based on the machine's intended usage. A well-maintained boom ensures optimal operational efficiency.
2. The Stick (Dipper)
The stick, also known as the dipper arm, connects the boom to the bucket. It allows for versatility in digging and reaching. The angle and length of the stick can be adjusted to perform different tasks, making it an essential component in excavation.
3. The Bucket
The bucket is the most recognizable part of the excavator, designed to scoop and carry materials. It comes in various shapes and sizes, tailored for particular tasks such as digging, grading, or demolition. Choosing the right bucket type ensures efficiency and effectiveness in your operations.
4. The House
The house is the upper structure that houses the operator's cab and the hydraulic controls. It can pivot 360 degrees, allowing the operator to maneuver the excavator with precision. Regular maintenance of the house enhances the longevity and functionality of the machine.
5. Hydraulic System
The heart of an excavator is its hydraulic system. This system includes various components such as the hydraulic pump, cylinders, and fluid reservoir. The hydraulic system powers the boom, stick, and bucket, providing the necessary force to perform heavy-duty tasks. Regular checks and maintenance of the hydraulic system are crucial for optimal performance.
6. Tracks or Wheels
Depending on the model, hydraulic excavators are equipped with either tracks or wheels. Tracks are ideal for rough terrains as they distribute weight evenly and enhance stability. Conversely, wheeled excavators offer increased mobility on paved surfaces. Maintaining the tracks or wheels ensures smooth operation on different terrains.
7. The Operator's Cab
The operator's cab is where the machine is controlled. It is equipped with various instruments and control systems for operating the excavator efficiently. Comfort and visibility are key factors in the design of the cab. Regular inspection of the cab components, including the windows and controls, contributes to operator safety and efficiency.
Importance of Maintaining Excavator Parts
Understanding the parts of hydraulic excavators also involves recognizing the importance of regular maintenance. Proper upkeep not only extends the life of your equipment but also prevents costly downtime. Here are some essential maintenance practices:
1. Regular Inspection
Conducting frequent inspections of all components, especially the hydraulic system and structural parts, helps detect issues early. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or leaks.
2. Fluid Checks
Hydraulic fluid levels should be monitored consistently to ensure the system operates efficiently. Low fluid levels can lead to hydraulic failure and increased wear on parts.
3. Keep Tracks and Wheels Clean
For tracked excavators, keeping the tracks clean from debris and mud is essential. For wheeled models, check the tires for wear and tear to ensure optimal traction and stability.
4. Lubricate Moving Parts
Regularly lubricating joints, bearings, and other moving parts reduces friction and prolongs the life of these components. Use high-quality lubricants recommended by the manufacturer.
5. Follow Manufacturer's Guidelines
Every excavator comes with a manufacturer's maintenance guide. Adhering to these guidelines is paramount for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment.
Common Problems with Hydraulic Excavators
As with any machinery, hydraulic excavators can experience a variety of issues. Awareness of these problems can help you address them promptly:
1. Hydraulic Leaks
One of the most common issues involves hydraulic leaks, which can significantly impact performance. Inspect hoses and fittings regularly to catch leaks early.
2. Worn Bushings and Pins
Over time, the bushings and pins connecting different parts may wear down, leading to inefficient operation and increased play in articulating components. Regularly check and replace worn parts to maintain precision.
3. Electrical Failure
Electrical issues can arise from faulty wiring, corroded connectors, or malfunctioning sensors. Regular electrical system checks can help prevent extensive damage.
Conclusion: Empower Your Excavator Knowledge
By understanding the parts of hydraulic excavators, their functions, and maintenance needs, you can enhance your operational efficiency and ensure the longevity of your machinery. Each component plays a critical role in the overall performance of an excavator and contributes to the success of your projects in categories like Auto Parts & Supplies and Motorcycle Parts & Supplies.
For more information on the parts and maintenance of hydraulic excavators, visit shophydraulicamerica.com to explore our range of products and services designed for optimal performance in your construction needs.